No other place is more critical for human survival than the Amazon. The Amazon basin harbors the largest remaining tropical forest on our planet and one-third of the planet’s biodiversity.
The Amazon is the world’s greatest reserve of life forms.
Threats
The region still faces several risks. Over the last 40 years, one-fifth of the Amazon rainforest has been cut down, and farms, ranches, and roads reach further into it each day.

One of Brazil’s most valuable assets is its dense covering of rain forests. The Amazon Rainforest is the most significant of these, covering a vast portion of the country and providing the ideal habitat to approximately one-third of all animal species in the world. To date, there have been identified approximately 56.000 species of plants 1.700 bird species, 695 amphibian species, 578 mammal and 651 reptile species. The Amazon rainforest cover almost 60% of the entire area of Brazil at 1.844,394 square miles or little less than 3 million square kilometers. Brazil is home to a third of the world’s rainforest, making it one of the most intriguing and beautiful lands on earth. The dense rainforest of Brazil consume an enormous amount of the world’s Carbon Dioxide and release Oxygen in return.

However, when destroyed, the trees release the Carbon as a greenhouse gas, with huge implications for earth and its atmosphere. Most of the rainforest areas in Brazil concentrated within the Amazon Basin, which is particularly humid, with year-round precipitation, making for the ideal ‘jungle’ environment. Unfortunately the deforestation by landowners, and multinational companies still largely without the control of authorities.

The deforestation and destruction of this priceless rainforest are the results of several illegal activities. If deforestation continues at its current rate, the entire Amazon Rainforest will be depleted by the end of the 21st century.

Deforestation
The main sources of deforestation in the Amazon are the human settlement and development of the land. Prior to the early 1960s, access to the forest’s interior was highly restricted, and the forest remained intact.Farms established during the 1960s based on crop cultivation and the slash and burn method. However, the colonists were unable to manage their fields and the crops because of the loss of soil fertility and weed invasion.The soils in the Amazon are productive for just a short period, so farmers are always moving to new areas and clearing more land. These farming practices led to deforestation and caused extensive environmental damage. Deforestation is considerable, and areas cleared of forest are visible to the naked eye from outer space or Google Earth.

In the 1970s, construction began on the Trans-Amazonian highway. This road represented a significant threat to the Amazon rainforest. Fortunately for the rainforest, the road has not been completed, reducing the environmental damage.

Between 1991 and 2000, the Amazon lost 587.000 square kilometers to become a pasture for cattle.The greatest concern is about the loss of its biodiversity as a result of the destruction of the forest and the acceleration of global warming. The Amazon rainforest could become unsustainable under conditions of severe reduce rainfall and increased temperatures.
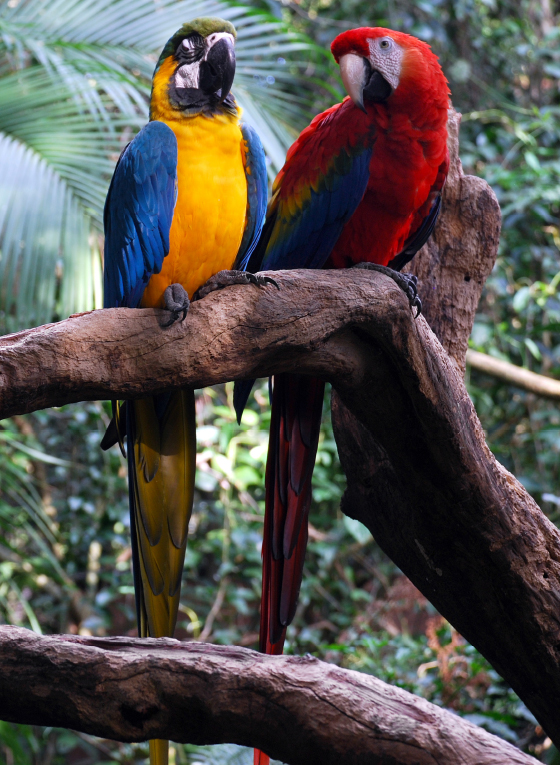
As the largest tract of tropical rainforest in the Americas, the Amazonian rainforest has unparalleled biodiversity. One in ten known species in the world lives in the Amazon rainforest.It has the largest collection of living plants and animal species in the world.
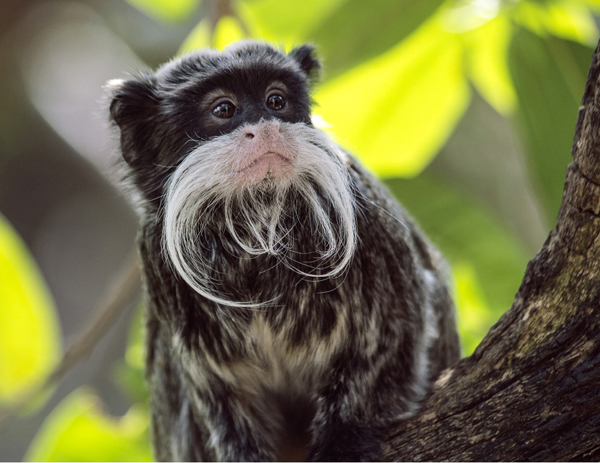

The region is home to about 2.5 million insect species, tens of thousands of plants, and some 2.000 birds and mammals. To date, at least 40.000 plant species, 2.200 fishes 1.294 birds, 427 mammals, 428 amphibians, and 378 reptiles have been scientifically classified in the region. One in five of all the bird species in the world live in the rainforest of the Amazon, and one in five of the fish species live in Amazonian rivers and streams. Scientists have described between 96.660 and 128.843 invertebrate species in Brazil alone.
Unrivaled biodiversity
The biodiversity of plant species is the highest on Earth with one 2001 study finding a quarter square kilometer (62 acres) of Ecuadorian rainforest supports more than 1.100 tree species. A study in 1999 found one square kilometer (247 acres) of Amazon rainforest can contain about 90.790 tons of living plants.To date, an estimated 438.000 species of plants of economic and social interest have been registered in the region with many more remaining to be discovered or cataloged.The total number of tree species in the region surpasses 16.000.
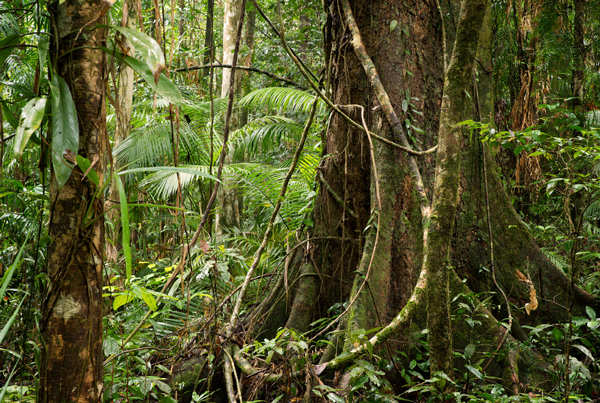

The green leaf area of plants and trees in the rainforest varies by about 25% as a result of seasonal changes. Leaves expand during the dry season when sunlight is at a maximum, then undergo abscission in the cloudy, wet season. These changes provide a balance of carbon between photosynthesis and respiration.
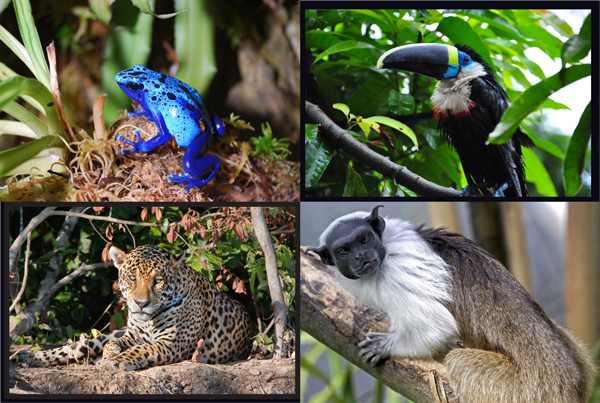

The rainforest contains several species that can pose a hazard. Among the largest predatory creatures are the black caiman, jaguar, cougar, and anaconda. In the river, electric eels can produce an electric shock that can stun or kill while “Piranha” a ferocious and carnivorous fish are known to bite and injure humans.Various species of poison dart frogs secrete toxins through their flesh. There are also numerous parasites and disease vectors. Vampire bats dwell in the rainforest and can spread the rabies virus. Malaria, yellow fever, and Dengue.
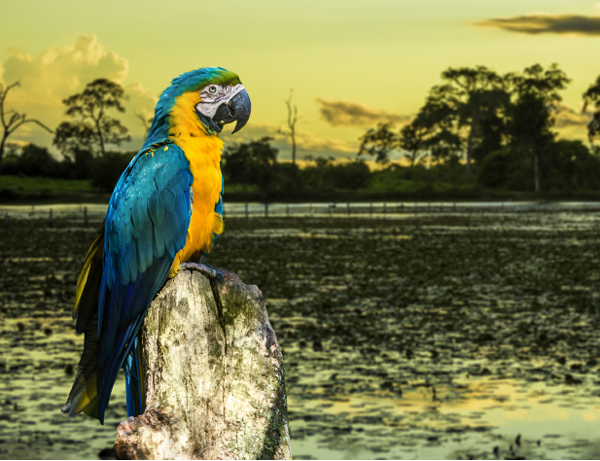

The beauty, mystery, and Amazon’s fauna has attracted scholars, environmentalists, adventurers, and tourists. And also has attracted those who don’t respect the Amazon as the last frontier of nature to the humankind.